How to Calculate Head Loss in a Pumping System
What is Head Loss and Why is it Important
Head loss refers to the total pressure losses sustained by the fluid as it flows from the suction point to the discharge point. Head loss is caused when the liquid loses momentum as it flows, and depends upon fluid viscosity, pipe diameter, pipe length and accessories such as valves and elbows within the pipework. Essentially, anything introduced into the path of the fluid will cause pressure loss. It is important to be able to work out the head loss that will be incurred within an installation in order to be able to determine the pressure required by the pump to operate efficiently.
How to Calculate Head Loss:
The calculation for working out the pressure loss within an installation is as follows:
Head Loss (Pc) = [Equiv. pipe length + Installation pipe length] x Pc % / 100 x Corrector
Please see below for guidance on the factors within the head loss calculation.
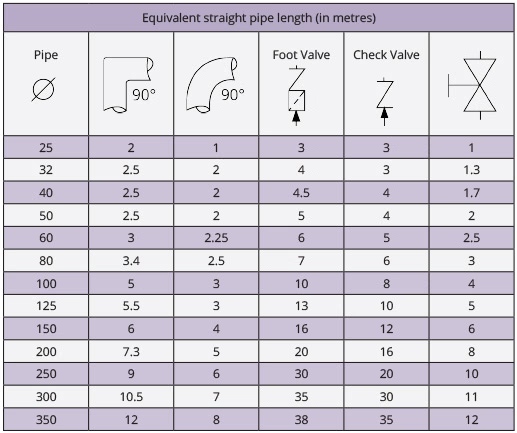
Equivalent pipe length
This refers to the equivalent length of the non-straight pipework when compared to straight pipes (in metres). The below table will help give you the figure considering the pipe diameter as well as the type of bends or valves installed inline.
Installation pipe length
This refers to the length of straight pipework installed (in metres). You should simply be able to measure this.
Pc % and Corrector
Please refer to the below table for these figures. If you click on the table, it will open in full size.
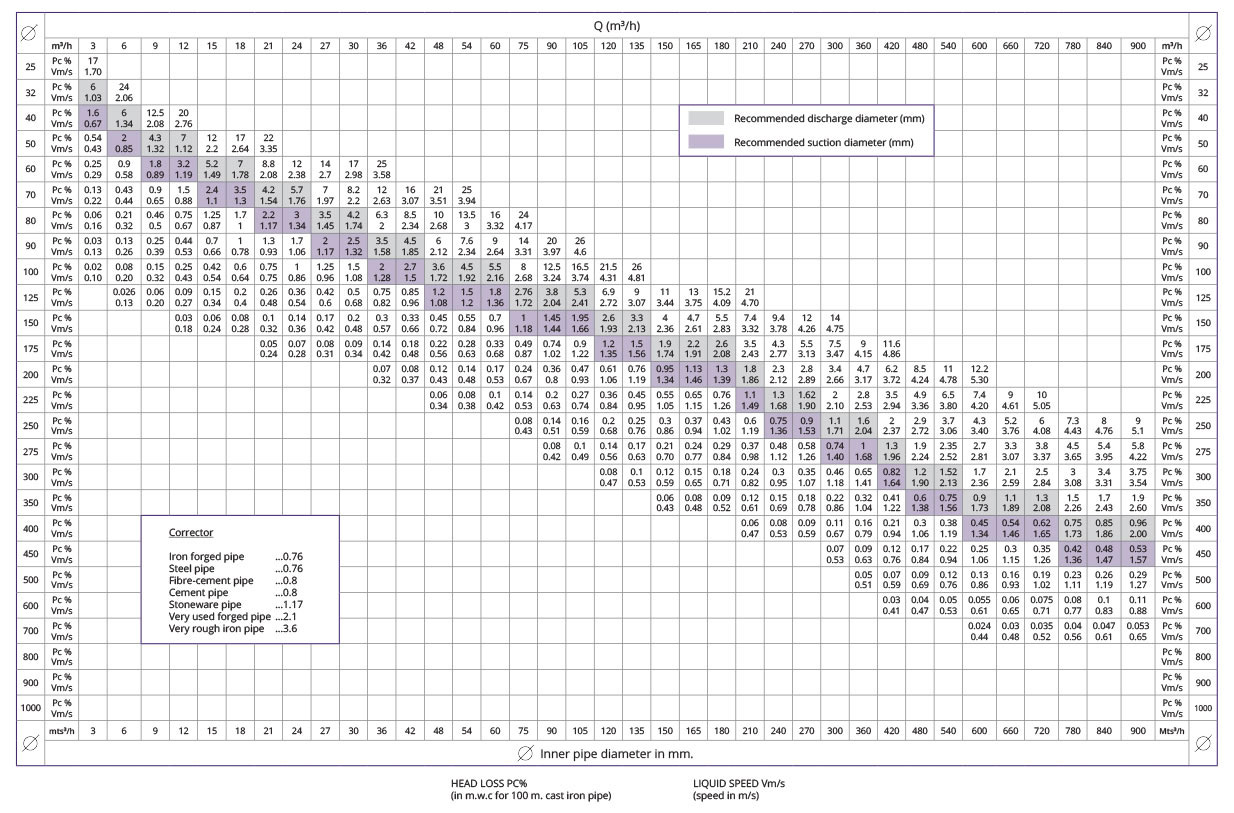
Please note: Recommended maximum head loss is around 6%
Need further guidance selecting your pump model?
Have an application you are trying to source a pump for and are struggling to work out the head loss of your installation? Speak to our pump experts today.


