Flexible Impeller Pump Guide
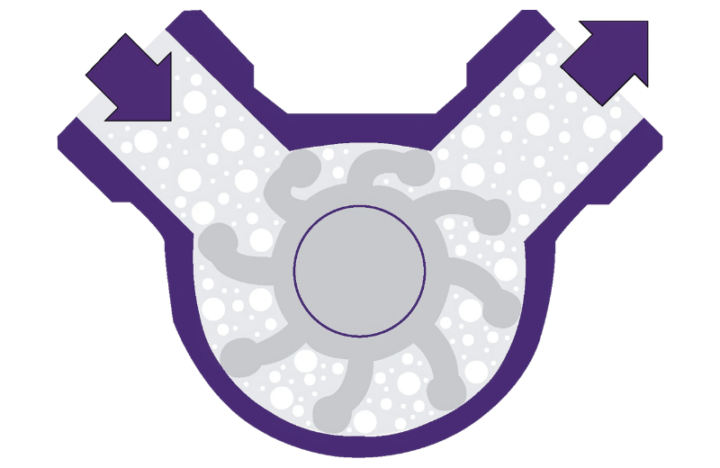
How do flexible impeller pumps work?
Flexible impeller pumps, also known as flexible vane pumps, are a form of positive displacement pump. The positive displacement family move fluid from the suction inlet by essentially trapping a specific amount of the fluid and then forcing it round into the outlet.
The flexible impeller pump working principle consists of a rotating rubber impeller with supple vanes attached that maintain contact with the pump inner walls. As the casing is actually smaller than the vanes, they must bend and then straighten as the impeller turns to conform to shape of the pump internal walls. The vacuum caused by the movement of these vanes push the fluid round from the inlet to the discharge pipe. As the space between each vane and the pump casing creates it's individual chamber, the flexible impeller pump head essentially has several chambers within in, all operating like valves. Hence, it's self-priming ability.
Design benefits
Variety of fluids – The impellers of flexible vane pumps are produced in various materials, making them compatible with a range of fluids. For example:
- Natural Rubber (NR) - For water based fluids, highest mechanical resistance.
- Neoprene (CR) - Good balance between chemical and mechanical resistance.
- Nitrile (NBR) – For foods, fats, fuels and oils..
- EPDM – Ideal for foods, hot fluids and clean in place applications, acids and alkaline.
- Silicon (VMQ) - Best for very high temperatures but low mechanical resistance.
As the impellers are made of a supple, rubber type material that is able to bend, flexible vane pumps are also able to handle viscous fluids and those with high solid content without causing damage. Compared to other pumps able to handle solids in suspension, flexible impeller pumps are a relatively low cost solution.
Excellent self-priming capabilities – Flexible impeller pumps are self-priming up to 6m from dry thanks to the nature of vanes meaning that they maintain a tight seal with the internal pump walls. As a result, this pump design is popular in installations where a good suction lift capacity is required such as the removal of fluid from sumps and the stripping of tanks, drums and IBCs, without the need for a non-return valve or manual priming on installation.
Smooth, low pulsating flow – The working principle of the flexible vane pump benefits from a steady pumping mechanism that results in the flow output being a lot smoother and gentler than other pumps without adhoc pressure spikes. The even flow rate makes it an ideal solution for filling, transfer and accurate dosing.
Reversible operation – Flexible impeller pumps are able to operate in both directions, which means that the pump itself can control the direction that the fluid moves. For example, when the transfer of liquid has finished, the pump can return any excess fluid sitting in the pipework to the container. It also makes it ideal for tank to tank transfer applications and enables the running through of cleaning fluid after use for Clean in Place.
Low shear operation – Flexible vane pumps are able to maintain their efficiency and priming ability even at low motor speeds. The low internal velocity of the operation as a result of the low RPM and gentle pumping mechanism means that shear sensitive fluids can be handled without any damage caused to their structure. Examples of shear sensitive fluids are food products such as olives that can be squashed, glues that can lose their stickiness or cream that can become thicker when agitated.
Various mounting positions – With the pump body being able to be installed in any position, the flexible impeller pump design is versatile enough to fit in all different types of pipework configurations. The benefit of this is that existing installations do not need to be adapted for the pump, as the pump can be fitted to meet the current pipework requirements.
Typical applications of a flexible vane pump
Flexible impeller pumps have pressure limitations that make them generally used within lower pressure installations. Their design benefits discussed above make them ideal units for the transfer, filling and dosing of a range of fluids, including delicate and shear sensitive products and liquids containing solids. Whilst viscous fluids can be handled, the capacity and suction lift capabilities of flexible vane pumps are affected by an increase in viscosity, which needs to be considered when the model is selected. For example, at 4000cP there is an approximate 60% pressure loss and maximum of 300rpm.
As the pump casing is often constructed of stainless steel and bronze, the flexible vane design is suitable for the hygienic and marine industries, making them commonly utilised in the following areas:

- Oenological (wine, stemmed grapes)
- Food processing (fruit pulp, honey, sauces and syrups)
- Dairy (creams, yoghurts, milk and liquid eggs)
- Cosmetics & pharmaceutical (shampoo, moisturisers, liquid soap)
- Shipping and marine (bilge water, ballast)
- Chemical & manufacturing (paint, water based glues, detergents)
- Fats, fuels, oils and lubricants
It is important however that the fluid in question is checked thoroughly against the selected impeller material compatibility chart.
Does this sound like what you need?
If from reading the above it sounds as though a flexible impeller pump is most suitable for your application in question, take a look at our range.



